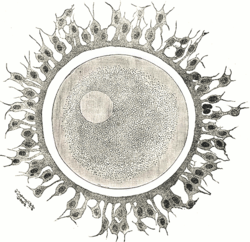
Zygote
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke") [1] is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes . The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring.
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
31135 characters 7 sections 11 paragraphs 1 images 83 internal links 18 external links |
zygote 0.522 cell 0.343 conceptus 0.241 embryo 0.186 fertilization 0.186 diploid 0.161 haploid 0.161 sperm 0.126 archegonium 0.120 meiosis 0.120 plants 0.120 tissues 0.120 implantation 0.103 cells 0.103 dna 0.093 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke") [1] is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes . The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring. |
|
| 2017 |
29272 characters 7 sections 11 paragraphs 1 images 79 internal links 12 external links |
zygote 0.522 cell 0.343 conceptus 0.241 embryo 0.186 fertilization 0.186 diploid 0.161 haploid 0.161 sperm 0.126 archegonium 0.120 meiosis 0.120 plants 0.120 tissues 0.120 implantation 0.103 cells 0.103 dna 0.093 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke"), [1] is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes . The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring. |
|
| 2016 |
26642 characters 7 sections 11 paragraphs 1 images 77 internal links 10 external links |
zygote 0.545 cell 0.358 conceptus 0.251 fertilization 0.194 diploid 0.168 archegonium 0.126 haploid 0.126 meiosis 0.126 plants 0.126 implantation 0.107 cells 0.107 sperm 0.105 embryo 0.097 dna 0.097 2n 0.084 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke"), [1] is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes . The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring. |
|
| 2015 |
25298 characters 7 sections 11 paragraphs 1 images 77 internal links 8 external links |
zygote 0.579 cell 0.381 conceptus 0.223 diploid 0.178 fertilization 0.172 cells 0.152 archegonium 0.134 plants 0.134 gamete 0.114 dna 0.103 2n 0.089 blastocyst 0.089 blastomeres 0.089 chloroplast 0.089 cpdna 0.089 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke"), [1] is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes . The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring. |
|
| 2014 |
21957 characters 4 sections 8 paragraphs 1 images 74 internal links 7 external links |
zygote 0.655 cell 0.345 cells 0.258 zygotes 0.201 archegonium 0.151 gamete 0.129 organisms 0.129 blastocyst 0.101 chloroplast 0.101 cleavage 0.101 cpdna 0.101 hertwig 0.101 morula 0.101 multicellular 0.101 plants 0.101 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke"), [1] is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction . In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo . In single-celled organisms, the zygote divides to produce offspring, usually through mitosis , the process of cell division. |
|
| 2013 |
22205 characters 4 sections 6 paragraphs 1 images 78 internal links 7 external links |
zygote 0.701 cell 0.369 cells 0.231 archegonium 0.162 zygotes 0.162 gamete 0.138 blastocyst 0.108 cleavage 0.108 morula 0.108 plants 0.108 divides 0.092 organisms 0.092 embryo 0.083 fertilization 0.083 divisions 0.083 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke"), [1] is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction . In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo . In single-celled organisms, the zygote divides to produce offspring, usually through Mitosis , the process of cell division. |
|
| 2012 |
20059 characters 5 sections 7 paragraphs 0 images 76 internal links 5 external links |
zygote 0.719 cell 0.308 cells 0.205 archegonium 0.180 zygotes 0.180 gamete 0.154 blastocyst 0.120 plants 0.120 divides 0.103 organisms 0.103 embryo 0.092 fertilization 0.092 dna 0.092 stage 0.076 sperm 0.075 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke"), [1] is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction . In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo . In single-celled organisms, the zygote divides to produce offspring, usually through meiosis . |
|
| 2011 |
18490 characters 3 sections 7 paragraphs 0 images 77 internal links 5 external links |
zygote 0.720 cell 0.308 cells 0.205 archegonium 0.180 zygotes 0.180 gamete 0.154 blastocyst 0.120 plants 0.120 divides 0.103 organisms 0.103 embryo 0.092 fertilization 0.092 dna 0.092 stage 0.076 sperm 0.075 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke"), [1] or zygocyte , is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction . In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo . In single-celled organisms, the zygote divides to produce offspring, usually through meiosis . |
|
| 2010 |
21655 characters 4 sections 6 paragraphs 0 images 86 internal links 5 external links |
zygote 0.594 twins 0.356 cell 0.282 zygotes 0.264 cells 0.169 fertilization 0.152 organism 0.132 pregnancies 0.132 twin 0.132 separated 0.102 dna 0.102 joined 0.086 identical 0.086 born 0.078 births 0.078 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke"), [1] or zygocyte , is the initial cell formed when a new organism is produced by means of sexual reproduction . A zygote is synthesized from the union of two gametes , and constitutes the first stage in a unique organism's development . Zygotes are usually produced by a fertilization event between two haploid cells—an ovum from a female and a sperm cell from a male —which combine to form the single diploid cell. Such zygotes contain DNA derived from both the mother and the father, and this provides all the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. The term zygote is also used more loosely to refer to the group of cells formed by the first few cell divisions, although this is properly referred to as a morula . |
|
| 2009 |
21128 characters 4 sections 6 paragraphs 0 images 80 internal links 5 external links |
zygote 0.594 twins 0.356 cell 0.282 zygotes 0.264 cells 0.169 fertilization 0.152 organism 0.132 pregnancies 0.132 twin 0.132 separated 0.102 dna 0.102 joined 0.086 identical 0.086 born 0.078 births 0.078 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zygōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zygoun "to join" or "to yoke"), [1] or zygocyte , is the initial cell formed when a new organism is produced by means of sexual reproduction . A zygote is synthesized from the union of two gametes , and constitutes the first stage in a unique organism's development . Zygotes are usually produced by a fertilization event between two haploid cells — an ovum from a female and a sperm cell from a male — which combine to form the single diploid cell. Such zygotes contain DNA derived from both the mother and the father, and this provides all the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. The term zygote is also used more loosely to refer to the group of cells formed by the first few cell divisions, although this is properly referred to as a morula . |
|
| 2008 |
19307 characters 4 sections 3 paragraphs 1 images 70 internal links 3 external links |
zygote 0.591 cell 0.379 fertilization 0.228 biparental 0.148 chlamydomonas 0.148 chloroplast 0.148 cpdna 0.148 diploid 0.148 haploid 0.148 pronuclei 0.148 yoke 0.148 yoked 0.148 zygotes 0.148 ζυγοῦν 0.148 ζυγωτός 0.148 |
A zygote (from Greek ζυγωτός zugōtos "joined" or "yoked", from ζυγοῦν zugoun "to join" or "to yoke") [1] is a cell that is the result of fertilization . That is, two haploid cells—usually an ovum from a female and a sperm cell from a male —merge into a single diploid cell called the zygote (or zygocyte ). |
|
| 2007 |
15676 characters 3 sections 7 paragraphs 1 images 72 internal links 1 external links |
zygote 0.613 cell 0.374 zygotes 0.350 fertilization 0.202 diploid 0.175 sperm 0.164 undergo 0.164 cycles 0.088 tube 0.088 biparental 0.088 chlamydomonas 0.088 chloroplast 0.088 cpdna 0.088 fusion 0.088 haploid 0.088 |
A zygote ( Greek : ζυγωτόν ) is a cell that is the result of fertilization . That is, two haploid cells—usually an ovum from a female and a sperm cell from a male —merge into a single diploid cell called the zygote (or zygocyte ). |
|
| 2006 |
12717 characters 0 sections 4 paragraphs 1 images 66 internal links 0 external links |
cell 0.657 zygote 0.307 zygotes 0.307 undergo 0.192 cycles 0.154 diploid 0.154 haploid 0.154 mitotic 0.154 fraternal 0.154 merge 0.154 cells 0.131 organisms 0.131 embryo 0.118 fertilization 0.118 divisions 0.118 |
A zygote ( Greek : ζυγωτόν ) is a cell that is the result of fertilization . That is, two haploid cells—usually (but not always) an ovum from a female and a sperm cell from a male —merge into a single diploid cell called the zygote (or zygocyte ). |
|
| 2005 |
6367 characters 1 sections 3 paragraphs 2 images 28 internal links 0 external links |
cell 0.695 zygote 0.325 undergo 0.203 cycles 0.162 diploid 0.162 haploid 0.162 mitotic 0.162 zygotes 0.162 fraternal 0.162 merge 0.162 cells 0.139 organisms 0.139 embryo 0.125 fertilization 0.125 divisions 0.125 |
A zygote ( Greek : ζυγωτόν ) is a cell that is the result of fertilization . That is, two haploid cells—usually (but not always) an ovum from a female and a sperm cell from a male —merge into a single diploid cell called the zygote (or zygocyte ). |
|
| 2004 |
4292 characters 1 sections 3 paragraphs 1 images 21 internal links 0 external links |
cell 0.697 zygote 0.326 undergo 0.204 cycles 0.163 diploid 0.163 haploid 0.163 mitotic 0.163 zygotes 0.163 fraternal 0.163 merge 0.163 cells 0.139 organisms 0.139 embryo 0.126 fertilization 0.126 divisions 0.126 |
A zygote is a cell that is the result of fertilization . That is, two haploid cells—usually (but not always) a sperm cell from a male and an ovum from a female —merge into a single diploid cell called the zygote . |
|
| 2003 |
1662 characters 0 sections 2 paragraphs 0 images 10 internal links 0 external links |
cell 0.677 zygote 0.396 cycles 0.198 diploid 0.198 haploid 0.198 merge 0.198 cells 0.169 organisms 0.169 embryo 0.152 fertilization 0.152 divisions 0.152 biology 0.152 ovum 0.141 pregnancy 0.131 sperm 0.124 |
|
|
| 2002 |
1361 characters 0 sections 1 paragraphs 0 images 7 internal links 0 external links |
zygote 0.492 cell 0.421 diploid 0.246 haploid 0.246 merge 0.246 destined 0.246 cells 0.211 cycle 0.190 embryo 0.190 fertilization 0.190 divisions 0.190 ovum 0.175 single 0.170 sperm 0.154 undergo 0.154 |
|
|
| 2001 |
867 characters 0 sections 1 paragraphs 0 images 0 internal links 0 external links |
zygote 0.433 combining 0.371 fertilization 0.334 divisions 0.334 ovum 0.308 sperm 0.271 undergo 0.271 entity 0.257 elements 0.245 multiple 0.188 single 0.150 female 0.106 result 0.093 male 0.079 |
Zygote is something that is result of fertilization that is combining female and male elements (sperm and ovum). This single entity is destinied to undergo a cyle of multiple divisions. |